Efficient Concrete Scanning Techniques for Construction Projects
Wiki Article
Beyond the Surface: Leveraging Advanced Concrete Scanning Techniques for Unmatched Precision and Understanding
In the realm of building and construction and facilities upkeep, the pursuit for accuracy and thoroughness is never-ending. Advanced concrete scanning strategies have actually emerged as essential devices in this quest, offering a glance beneath the surface area to unveil a world of crucial understandings. By taking advantage of innovative modern technologies, specialists can uncover anomalies, analyze the problem of concrete structures, and make notified decisions that form the program of jobs. The effects of these methods extend much past plain surface-level evaluations, guaranteeing a deepness of accuracy and understanding that is unparalleled.Value of Advanced Concrete Scanning
The value of making use of innovative concrete scanning strategies lies in the unequaled precision they supply for identifying sub-surface anomalies and ensuring architectural honesty. By utilizing cutting-edge technologies such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR), electro-magnetic induction, and advanced sonar imaging, building and construction specialists can dig beneath the surface area of concrete frameworks with a level of precision that far surpasses conventional assessment techniques. Concrete Scanning. These techniques allow the identification of covert risks like rebar corrosion, voids, conduits, or post-tension wires that could jeopardize the stability and safety and security of a framework graduallyFurthermore, advanced concrete scanning provides important understandings into the overall problem of a concrete aspect without the need for intrusive actions, reducing the threat of causing damages during the evaluation process. The ability to identify the precise place and depth of prospective issues enables targeted repairs and upkeep, inevitably extending the lifespan of the framework and enhancing its performance. Basically, the relevance of advanced concrete scanning can not be overemphasized in the realm of construction and framework maintenance, where accuracy and reliability are extremely important.
Kinds Of Cutting-Edge Technologies
Abnormalities and Flaw Discovery
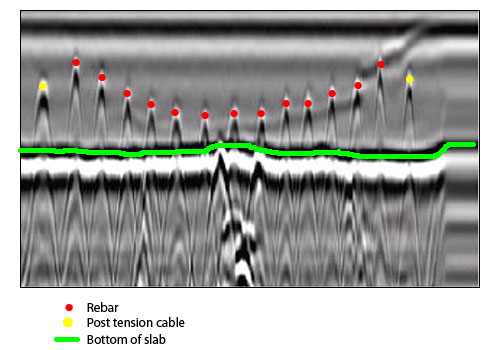
In addition to GPR, concrete scanning methods like thermography and impact-echo testing are also reliable in detecting abnormalities and problems. Thermography uses infrared modern technology to determine variations in surface area temperature level, showing potential locations of worry such as delamination or moisture ingress. On the various other hand, impact-echo testing includes assessing acoustic actions to detect gaps, fractures, and various other issues within the concrete. By leveraging these advanced methods, experts can proactively attend to structural problems, making sure the long life and security of concrete frameworks.
Assessing Concrete Condition
Just how can engineers properly assess the condition of concrete structures to ensure their longevity and safety? Examining the concrete problem is an important facet of preserving framework stability. Various advanced concrete scanning techniques are used for this objective. Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is typically utilized to examine the internal framework of concrete, finding voids, splits, and various other anomalies that may jeopardize its toughness. Additionally, impact-echo testing can provide insights into the thickness and stability of concrete elements. Ultrasonic pulse speed screening is an additional useful approach for reviewing concrete top quality by gauging the rate of sound waves via the material.Incorporating non-destructive testing methods with visual assessments enables for a thorough analysis of concrete problem, enabling designers to determine possible problems early on and carry out prompt maintenance or fixings. By leveraging these innovative strategies, engineers can ensure the long-lasting toughness and safety and security of concrete structures.
Enhancing Decision-Making Processes
In the world visit this page of infrastructure management, optimizing decision-making procedures is imperative for guaranteeing the reliable maintenance and long life of concrete frameworks. Enhanced decision-making procedures in concrete administration involve using innovative scanning methods to collect detailed information on the problem of frameworks. By leveraging modern technologies such as ground-penetrating radar and 3D imaging, stakeholders can make informed decisions pertaining to support, repair work, or substitute approaches.These progressed scanning methods provide vital insights right into the internal structure of concrete, identifying potential issues such as gaps, fractures, or corrosion that may not be noticeable on the surface. This level of comprehensive info enables positive upkeep preparation, decreasing the danger of architectural failures and enhancing the general lifespan of concrete frameworks.
In addition, by including electronic documents and evaluation tools into the decision-making process, stakeholders can track the advancement of concrete conditions in time, enabling predictive upkeep methods and enhancing source appropriation. Inevitably, the assimilation of innovative concrete scanning methods enhances decision-making processes by giving unmatched precision, insight, and efficiency in infrastructure administration.
Conclusion
Finally, advanced concrete scanning techniques supply unequaled precision and insight in identifying abnormalities, issues, and analyzing the problem of concrete structures. By leveraging innovative innovations, decision-making processes can be enhanced, bring about more enlightened and reliable options for keeping and fixing concrete facilities. These methods play a vital function in making certain the security and longevity of concrete frameworks, making them an indispensable device in the field of building and construction and design.In addition, progressed concrete scanning offers important understandings right into the total problem of a concrete component without the demand for invasive procedures, decreasing the danger of creating damage throughout the evaluation procedure - Concrete Scanning. One more innovative innovation is 3D X-ray scanning, which supplies thorough images of the inner framework of concrete, offering important info without the requirement for damaging screening. Additionally, Concrete Cover Meters are utilized to from this source measure the density of concrete cover over reinforcement bars properly. Enhanced decision-making procedures in concrete click this site management include utilizing innovative scanning techniques to gather comprehensive information on the problem of structures.In conclusion, progressed concrete scanning techniques provide unequaled accuracy and insight in discovering abnormalities, defects, and assessing the problem of concrete structures
Report this wiki page